Introduction
In today’s highly competitive global market, businesses are increasingly dependent on technology to drive efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. At the heart of this digital transformation is the Business Inventory System (BIS)—a pivotal tool that manages the lifecycle of a company’s stock. Whether you’re running a small retail shop, a manufacturing unit, or a large e-commerce platform, having an effective inventory management system is crucial to your operational success.
This article explores what a Business Inventory System is, its components, benefits, and types, as well as modern trends shaping its evolution. We’ll also provide insights into how businesses can choose the right inventory system and the common challenges faced during implementation.
What Is a Business Inventory System?
A Business Inventory System is a software or method used to track goods, materials, and products that a company sells or uses in production. It is designed to monitor inventory levels, manage reordering, forecast demand, and ensure the smooth flow of items throughout the supply chain.
An efficient BIS not only helps avoid stockouts and overstocking but also ensures that the right products are available at the right time and place. It integrates with other systems such as point-of-sale (POS), accounting, warehouse management, and customer relationship management (CRM) to create a seamless workflow.
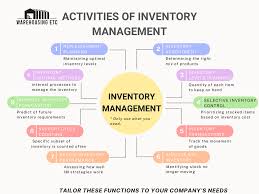
Key Components of a Business Inventory System
A robust inventory system is made up of several integral components:
1. Inventory Tracking
This module tracks every product or item from the moment it enters the inventory until it is sold or used. Tracking can be done using:
-
Barcodes
-
RFID tags
-
QR codes
-
Serial numbers
2. Stock Management
Stock management involves maintaining optimal inventory levels and ensuring that stock is neither too low nor too high. This component helps with:
-
Setting reorder points
-
Tracking stock location
-
Managing stock across multiple warehouses
3. Order Management
This module streamlines the entire order cycle, from purchase to delivery. It includes:
-
Purchase orders (POs)
-
Sales orders
-
Supplier and vendor management
4. Inventory Forecasting
Advanced systems use data analytics and machine learning to forecast future demand based on:
-
Historical data
-
Seasonal trends
-
Market behavior
5. Reporting and Analytics
Real-time reports help in making data-driven decisions. Common reports include:
-
Inventory valuation
-
Turnover ratios
-
Shrinkage rates
-
Stock aging reports
6. Integration Capabilities
An efficient system should integrate with:
-
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
-
POS (Point of Sale)
-
E-commerce platforms
-
Financial software like QuickBooks or SAP
Types of Business Inventory Systems
Different businesses have different inventory needs. There are two main types of inventory systems:
1. Periodic Inventory System
In this system, inventory levels are updated at specific intervals—monthly, quarterly, or yearly. It is suitable for small businesses with limited stock movement.
Pros:
-
Low implementation cost
-
Simple to manage
Cons:
-
Lack of real-time tracking
-
Inaccuracy in stock levels
2. Perpetual Inventory System
This system continuously updates inventory records in real time. It is widely used in modern retail and e-commerce.
Pros:
-
Real-time accuracy
-
Automatic alerts and updates
Cons:
-
Higher implementation costs
-
Requires training and IT support
Why Businesses Need an Inventory System
Inventory is often the largest current asset of a company. Poor inventory management can lead to:
-
Cash flow problems
-
Customer dissatisfaction
-
High carrying costs
-
Loss due to theft or damage
Here’s why businesses should invest in a reliable inventory system:
1. Operational Efficiency
Automating inventory tasks reduces manual labor and human errors, enabling employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
2. Cost Reduction
A BIS helps identify slow-moving items, reduce holding costs, and minimize waste or obsolescence.
3. Improved Customer Satisfaction
With the right products available at the right time, businesses can fulfill orders quickly and accurately, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
4. Better Decision Making
Access to real-time data helps managers make informed decisions regarding purchasing, pricing, and promotions.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Inventory systems assist in maintaining accurate records for auditing, taxation, and regulatory purposes.
How to Choose the Right Business Inventory System
Selecting the appropriate BIS requires careful consideration. Here’s a guide to help businesses make the right choice:
1. Assess Your Needs
Determine the size of your inventory, the complexity of your supply chain, and the level of automation required.
2. Scalability
Choose a system that can grow with your business, supporting additional products, locations, and users.
3. Ease of Use
The user interface should be intuitive and require minimal training.
4. Integration
Ensure compatibility with existing tools like POS, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
5. Support and Maintenance
Check the vendor’s reputation for customer support, updates, and technical assistance.
6. Cost
Consider the total cost of ownership, including setup, subscription, training, and support fees.
Top Business Inventory Systems in 2025
Several inventory systems have stood out in 2025 for their innovative features and robust performance:
1. NetSuite ERP
A cloud-based solution suitable for medium to large businesses. Offers full integration with CRM, financials, and e-commerce.
2. Zoho Inventory
Great for small to medium-sized businesses. Offers barcode scanning, order management, and multi-channel selling.
3. TradeGecko (Now QuickBooks Commerce)
Ideal for e-commerce and wholesale businesses. Integrates seamlessly with Shopify, Amazon, and WooCommerce.
4. Fishbowl Inventory
An affordable solution that works well with QuickBooks and provides manufacturing and warehouse management capabilities.
5. Odoo Inventory
An open-source ERP solution offering flexible customization for businesses of all sizes.
Future Trends in Business Inventory Systems
As technology continues to evolve, inventory systems are becoming more intelligent, automated, and user-friendly. Here are the key trends defining the future:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-driven inventory systems can predict demand, optimize stock levels, and even suggest procurement strategies.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT sensors and devices allow real-time inventory tracking with minimal human intervention.
3. Blockchain
Blockchain ensures transparency and traceability in the supply chain, preventing fraud and improving supplier accountability.
4. Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud inventory systems offer real-time access from anywhere, reducing infrastructure costs and improving collaboration.
5. Mobile Inventory Management
Mobile apps allow staff to update inventory on the go using smartphones or tablets, improving flexibility and speed.
Challenges in Implementing an Inventory System
Despite the many benefits, businesses often face obstacles when adopting a BIS:
1. Resistance to Change
Employees may resist new technologies, fearing job loss or complexity.
2. High Initial Costs
Purchasing software, hardware, and training staff can be expensive, especially for small businesses.
3. Data Migration
Transferring existing inventory data into a new system can be tedious and prone to errors.
4. Integration Issues
Incompatibility with legacy systems may require additional customizations or third-party plugins.
5. Security Concerns
Cloud-based systems must be secured against data breaches and cyber threats.
Best Practices for Effective Inventory Management
To get the most out of your BIS, follow these best practices:
-
Conduct regular audits to reconcile system data with physical stock.
-
Set clear policies for inventory handling, returns, and reorders.
-
Train employees regularly on how to use the system efficiently.
-
Use ABC analysis to prioritize high-value inventory.
-
Monitor KPIs such as turnover rates and order accuracy.
-
Automate where possible to reduce manual entry and human error.
Real-World Example: Walmart
Walmart is a prime example of using an advanced BIS to its advantage. With thousands of products and suppliers globally, Walmart uses AI-driven forecasting and RFID tagging to track inventory in real time. This not only reduces waste and shrinkage but also enhances customer satisfaction through optimized shelf stocking and minimal stockouts.
Conclusion
In an era where speed, accuracy, and efficiency are critical for success, a Business Inventory System is not just a tool—it’s a strategic asset. It empowers businesses to gain control over their inventory, streamline operations, and make smarter decisions. As inventory systems become more intelligent and interconnected, businesses that adopt and adapt to these technologies will gain a substantial edge over their competitors.
Whether you’re a startup or a multinational corporation, investing in the right inventory system is a step toward sustainable growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term profitability.